The immune system defends the body from deadly invaders. The immune system detects a wide variety of agents and distinguishes them from healthy tissue. Most people refer to these invaders as “germs.” Germs may damage healthy tissue both directly, and by depleting essential nutrients from the body below critical levels. Once critically depleted, cells and tissues function improperly, furthering the downward spiral of illness towards death.
The way I look at the relationship, it is the failure of an undernourished immune system that results in disease—not just the presence of germs.
A healthy immune system requires many nutrients, including vitamin C (1). Healthy neutrophils and macrophages (types of white blood cells in the immune system) contain 1 mM concentrations of vitamin C—that’s 50-100 times higher than the concentration of vitamin C in the plasma (liquid part of the blood). A healthy person produces about 100 billion neutrophils per day. However, when the immune system detects germs and swings into action to destroy the invaders, its white blood cell production—and its need for vitamin C—increases (2).
Leukocytes (white blood cells) are a major arm of the immune system. Leukocytes include the phagocytes (macrophages, neutrophils, and dendritic cells), innate lymphoid cells, mast cells, eosinophils, basophils, and natural killer cells. These cells identify and eliminate pathogens, either by attacking pathogens through contact or by engulfing and then killing them. These actions require vitamin C. Activation of neutrophil and monocyte oxidative bursts to kill germs alters the cell membranes to “pull in” dehydroascorbic acid and ascorbic acid from the blood to increase the vitamin C concentration within these cells ten-fold (from 1 mM to 10 mM).
The Linus Pauling Institute lists specific measures of functions stimulated by vitamin C as including cellular motility, chemotaxis and phagocytosis. Neutrophils, mononuclear phagocytes, and lymphocytes accumulate vitamin C to high concentrations, which can protect these cell types from oxidative damage.
Vitamin C, through its antioxidant functions, including regeneration of glutamine and vitamin E, has been shown to protect leukocytes from self-inflicted oxidative damage (3).
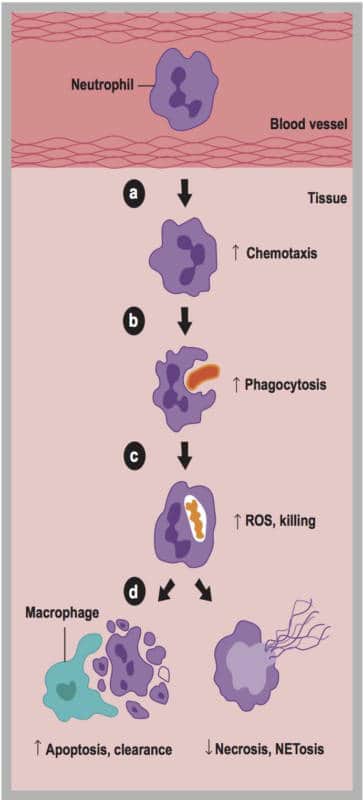
The 2000 RDA’s by the Institute of Medicine teaches us that high intracellular concentration of ascorbate in leukocytes provides cellular protection against oxidant damage associated with the respiratory burst that plays a major role in the immune system (4). The respiratory burst (also called oxidative burst) is the rapid release of reactive oxygen species from various immune system cells. This rapid release kills invaders such as viruses. However, without adequate vitamin C, the immune cells would be unable to generate sufficient amounts of the reactive oxygen species needed to kill germs. Even worse, in severe vitamin C deficiency, the immune cells themselves would also be destroyed. As Michael Passwater, MT(ASCP) SBB, DLM, CSSGB (ASQ), stated in our interview on vitamin C and sepsis, “If neutrophils (a type of white blood cell) lack vitamin C, they self-destruct. Instead of fighting the infection or clearing and rebuilding injured tissue, its internal peroxides and enzymes are released, damaging the surrounding tissue—like a firefighter using a flamethrower on a house fire” (5).
Vitamin C is more than an antiviral. The reported deaths from the COVID-19 virus have involved multi-organ failure, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), and pneumonia. Paul E. Marik, M.D., and others have shown IV vitamin C to be effective against these conditions in sepsis (6).
In summary, it is a long-proven and uncontested fact that vitamin C has several nutritional functions, including supporting the immune system. As a dietary supplement, legally it can be stated that vitamin C “supports” a normal immune function.If someone is in the business of selling vitamin C, they can’t legally refer to any disease function—including scurvy. It’s best to suggest that anyone interested in vitamin C and any disease check with an appropriately informed physician or with an educator such as Dr. Andrew W. Saul.
In the clinic, it appears, based on dramatic successful case studies, that the relationship between vitamin C in the cells and immune function is a continuum, with a steady supply of higher levels of vitamin C allowing immune cells to sustain optimal function during the battle against invaders and through recovery. However, it would be helpful to confirm this with randomized double-blind trials.
Anyone selling vitamin C as a dietary supplement must follow the FDA regulation that any claim of a substance treating a disease makes that product an illegal unproven drug, which would have serious consequences to the seller. This is capricious and arbitrary, but it is the regulation, and, in my humble opinion, it seems to work to help reduce chaos and possible fraud in the dietary supplement category. While the regulation is far from being perfect, it provides some protection to both consumers and the supplement industry alike.
The medical profession, on the other hand, can legally treat diseases. Many physicians through the decades have successfully used high-dose vitamin C to treat diseases, including viruses. With so many lives at stake, It is important to educate everyone—the medical profession and laypersons alike—about the safe and effective use of vitamin C as well as the nutritional functions of vitamin C. Therefore, I am calling on Dr. Andrew W. Saul, once again, to educate our readers, laypersons, nutritionists, and physicians on treating viruses with vitamin C.
Dr. Saul has been an orthomolecular medical writer and lecturer for more than 40 years. Dr. Saul has taught clinical nutrition at New York Chiropractic College and postgraduate continuing education programs. He was also on the faculty of the State University of New York for nine years. Two of those years were spent teaching for the University in both women’s and men’s penitentiaries.
Dr. Saul is editor-in-chief of the Orthomolecular Medicine News Service (OMNS) and has published over 200 peer-reviewed articles. His bestselling book Doctor Yourself has been translated into eight languages. He has written a dozen other books, four of which are coauthored with Abram Hoffer, M.D. Dr. Saul's educational website iswww.DoctorYourself.com, the largest peer-reviewed, non-commercial natural healing resource on the internet. He is a board member of the Japanese College of Intravenous Therapy. Dr. Saul was inducted into the Orthomolecular Medicine Hall of Fame in 2013. He is featured in the documentaries “FoodMatters” and “That Vitamin Movie” (www.thatvitaminmovie.com).
Passwater:Dr. Saul, thank you once again for educating our readers on vitamin C and health. You recently issued several press releases via the Orthomolecular Medicine News Service about vitamin C and COVID-19 (a current pandemic coronavirus). Do you know if anyone is following up with a clinical study?

Saul:There are at least three hospital-based clinical studies going on right now in China. I am in daily contact with one of the key researchers, Richard Cheng, M.D., Ph.D.
Dr. Cheng, who is a U.S. board-certified specialist in anti-aging medicine, early on in the outbreak stated, "Vitamin C is very promising for prevention, and especially important to treat dying patients when there is no better treatment. Over 2,000 people have died of the COVID-19 outbreak and yet I have not seen or heard large dose intravenous vitamin C being used in any of the cases. The current sole focus on vaccines and specific antiviral drugs for epidemics is misplaced."
Dr. Cheng has also said, “I have been calling for the use of large-dose IV vitamin C for the treatment of coronavirus (COVID-19) patients, and also for oral vitamin C for the milder cases, or for the prevention of this disease.” He is dialoguing with more physicians and hospitals as you read this.
I am a member of the Medical and Scientific Advisory Board to the International Intravenous Vitamin C China Epidemic Medical Support Team. Dr. Cheng is its director. The associate director is Hong Zhang, Ph.D. My good friend and colleague Thomas E. Levy, M.D., JD is also on the board.
Details of the Wuhan protocol in English are posted at:www.orthomolecular.org/resources/omns/v16n07.shtml
Protocol in Chinese:www.doctoryourself.com/Coronavirus_Chinese_IV_C_Protocol.pdf
The first approved study of IV vitamin C against COVID-19 involves 12,000 to 24,000 mg/day of vitamin C by IV. Dr. Cheng also specifically calls for immediate use of vitamin C for prevention of coronavirus (COVID-19):www.youtube.com/watch?v=TC0SO9KDG7U
A second clinical trial of intravenous vitamin C was announced in China on February 13. In this second study, says Dr. Cheng, “They plan to give 6,000 mg/day and 12,000 mg/day per day for moderate and severe cases. We are also communicating with other hospitals about starting more intravenous vitamin C clinical studies. We would like to see oral vitamin C included in these studies, as the oral forms can be applied to more patients and at home.” Additional information can be found at:www.orthomolecular.org/resources/omns/v16n11.shtml
On Feb 21, 2020, a third clinical trial for intravenous vitamin C for COVID-19 was announced:www.youtube.com/watch?v=VMDX0RSDp1k.
In addition, Vitamin C is now being used to prevent and treat COVID-19 in China and in Korea. And it is working.
Here is a verified official statement from China's Xi'an Jiaotong University Second Hospital:"On the afternoon of February 20, 2020, another 4 patients with severe coronavirus pneumonia recovered from the C10 West Ward of Tongji Hospital. In the past 8 patients have been discharged from hospital...[H]igh-dose vitamin C achieved good results in clinical applications. We believe that for patients with severe neonatal pneumonia, and for critically ill patients, vitamin C treatment should be initiated as soon as possible after admission. Numerous studies have shown that the dose of vitamin C has a lot to do with the effect of treatment. High-dose vitamin C can not only improve antiviral levels, but more importantly, can prevent and treat acute lung injury (ALI) and acute respiratory distress (ARDS)."
Here is a report from Korea:"At my hospital in Daegu, South Korea, all inpatients and all staff members have been using vitamin C orally since last week. Some people this week had a mild fever, headaches and coughs, and those who had symptoms got 30,000 mg intravenous vitamin C. Some people got better after about two days, and most had symptoms go away after one injection." (Hyoungjoo Shin, M.D.)
It is now the official recommendation of the government of Shanghai, China that COVID-19 should be treated with high amounts of intravenous vitamin C.(https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/bF2YhJKiOfe1yimBc4XwOA)
Dr. Cheng discusses a case study in which vitamin C was successful against COVID-19 in a family of six athttps://www.brighteon.com/32df0202-facb-443a-8ef6-5648b4b2f9ec.
Passwater:It appears that Dr. Cheng is getting the message about vitamin C and the nutritional need for keeping the immune system optimally functional out to the Chinese people.
Saul: Yes. The photo in Figure 2 is verification of this. The photo is from a DSM announcement on Facebook in February. It shows a truck loaded with 50 tons of vitamin C from the DSM plant in Jiangshan to be delivered to the people of the Province of Hubei of which Wuhan is the capital.
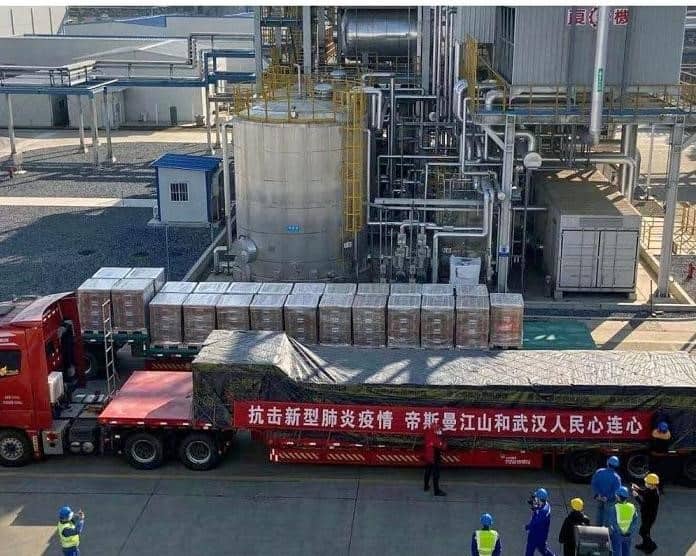

Passwater:50 tons!
Saul:Yes, 50 tons! The translation of the banner on the truck is “In the fight against N-CoV, the people of DSM Jiangshan and Wuhan are heart to heart.”
Passwater:What are the recommendations made in the OMNS press releases?
Saul:As therapy for hospitalized patients in China, at least 12,000 to 24,000 mg/day intravenous vitamin C.
For prevention, the physicians of the Orthomolecular Medicine News Service Review Board recommend the following:
- At least 3,000 milligrams (preferably more) of vitamin C daily, in divided doses. Vitamin C empowers the immune system and can directly denature many viruses. To be most effective, it should be taken to bowel tolerance. This means taking high doses several times each day.
- Magnesium: 400 mg daily (in citrate, malate, chelate, or chloride form).
- Vitamin D3: 2,000 International Units daily (starting with 5,000 IU/day for two weeks, then reduce to 2,000).
- Zinc: 20-40 mg/day for adults.
- Selenium: 100 mcg (micrograms) daily.
- B-complex vitamins and vitamin A: A multivitamin tablet with each meal will supply these conveniently and economically.
Passwater:Where can physicians find the specific IV formula to use?
Saul:Physicians can make the vitamin C IV solution themselves by following Dr. Robert F. Cathcart’s instructions, which can be found atwww.doctoryourself.com/vitciv.html.Any compounding pharmacy can prepare it. Any hospital pharmacy can prepare it. And don’t let them try to tell you they can’t. May I add a commonsense but important caution to your readers that intravenous or intramuscular vitamin C should only be administered by a licensed health professional.
Passwater:Such a clinical trial can’t cost much, and the results would be seen quickly. Drug companies have no interest in studying an unpatentable nutrient, but couldn’t the government or a university be willing to test this inexpensive and readily available nutrient?
Saul:Some already are. For example, Professor Qi Chen, Ph.D., and Professor Jeanne Drisko, M.D., both of the Kansas University Medical School, are actively interested in this matter.
Atsuo Yanagisawa, M.D., Ph.D., Professor of Clinical Medicine at the Kyorin University School of Health Sciences, states: “Patients with acute viral infections show a depletion of vitamin C. Such patients should be treated by adding vitamin C, via oral or IV, to neutralize free radicals, maintain physiological functions, and enhance natural healing. The Japanese College of Intravenous Therapy [JITC] recommends that our 850 physician members stock extra vitamin C vials in case of a pandemic. JCIT recommends intravenous vitamin C (IVC) 12,000 mg to 25,000 mg for acute viral infections. IVC is usually administered once or twice a day for 2-5 continuous days.” To read the complete JCIT protocol in English:www.orthomolecular.org/resources/omns/v16n07.shtml.
There is no need for delay. The recently passed federal “Right to Try” act makes it possible for patients to demand “unapproved” treatments now, and safeguards hospitals and physicians who provide them.www.righttotry.org/rtt-faq/
Passwater:Many of our readers are familiar with the publications of physicians such as Fred Klenner, M.D., against polio. Please tell our readers about the teachings of others including Dr. Cathcart. What other conditions should be treated with high-dose vitamin C?
Saul:Virtually all viral illness is treatable with adequately enormous quantities of vitamin C. Over time, as his experience as a physician continued, Dr. Robert Cathcart actually stopped using viral disease names. He just called this viral illness a 60-gram (60,000 mg) cold and that one a 150-gram (150,000 mg) cold. Treatment was based on the amount of C that cured the illness. That is medical brilliance.
Although the most effective dose is truly high, even a low supplemental amount of vitamin C may help save lives. This is very important for those with low incomes and few treatment options. For example, in one well-controlled, randomized study, just 200 mg/day vitamin C given to the elderly resulted in improvement in respiratory symptoms in the most severely ill, hospitalized patients (5). And there were 80% fewer deaths in the vitamin C group. But to best build up our immune systems, we need to employ large, orthomolecular doses (7).
Wikipedia actually deleted existing well-referenced biographical pages of both of these historically important 20th century physicians, Frederick Robert Klenner, M.D., and Robert Fulton Cathcart III, M.D. Over decades of practice and reported in medical journals, both doctors used very high doses of vitamin C to cure serious viral illnesses. It is a moral outrage that in a time of viral emergency, physicians’ professional opinions, and indeed all information about those physicians’ therapies, is being kept from the public.
Passwater:Is there suppression of this information?
Saul:Yes. The World Health Organization (WHO) has met with Google, Facebook and other information-access purveyors specifically to stop the spread of alternative health care information about COVID-19. Anyone saying that vitamin therapy can stop coronavirus is already being labeled as “promoting false information” and promulgating “fake news.” Even the sharing of verifiable news and direct quotes from credentialed medical professionals is being restricted or blocked on social media. You can see sequential examples of this atwww.facebook.com/themegavitaminman. I am glad to have this opportunity to share this information with your readers.
Passwater:It’s our moral duty to inform and educate. Our readers have a right to know the facts. That’s why I was awarded the Zenger Award for Press Freedom in 2004. Where can readers find more information on vitamin C and viruses?
Saul:The best way is to look at the exact treatment plans doctors are employing, right now, in China. Go to those actually doing it. When I was a boy, my father told me, “Andrew, when you want to know something, ask the organ grinder, not the monkey.” Instructions by physicians who are experienced with high-dose vitamin C treatment of viral diseases are the most helpful resource on the internet. Detailed protocols are posted for free access athttp://orthomolecular.org/resources/omns/v16n07.shtml(IV vitamin C);http://orthomolecular.org/resources/omns/v16n06.shtml(vitamin C and additional nutrients); andwww.doctoryourself.com/cathcart_C_summary.html(oral high dosing of vitamin C).
Passwater: I also recommend readers read the article by Drs. Nabzdyk and Bittner (8). Dr. Saul, thank you for educating our readers once again.
References
- Jacob RA, Sotoudeh G. Vitamin C function and status in chronic disease. Nutr Clin Care 2002;5:66-74.
- Carr AC, Frei B. Toward a new recommended dietary allowance for vitamin C based on antioxidant and health effects in humans. Am J Clin Nutr 1999;69:1086-107.
- https://lpi.oregonstate.edu/mic/vitamins/vitamin-C.
- Institute of Medicine. 2000. Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin C, Vitamin E, Selenium, and Carotenoids. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press. https://doi.org/10.17226/9810.
- https://wholefoodsmagazine.com/columns/vitamin-connection/vitamin-c-sepsis-and-blood-vessel-health/
- https://wholefoodsmagazine.com/columns/vitamin-connection/the-marik-protocol-for-deadly-sepsis-is-already-saving-many-lives-the-roles-of-vitamins-c-and-b1-thiamine/
- Hunt C et al. Int J Vitam Nutr Res 1994;64:212-19.
- Nabzdyk CS, Bittner EA. Vitamin C in the critically ill -indications and controversies. World J Crit Care Med 2018; 7(5):52-61 Available from: URL: http://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3141/full/v7/i5/52.htm DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.5492/wjccm.v7.i5.52










