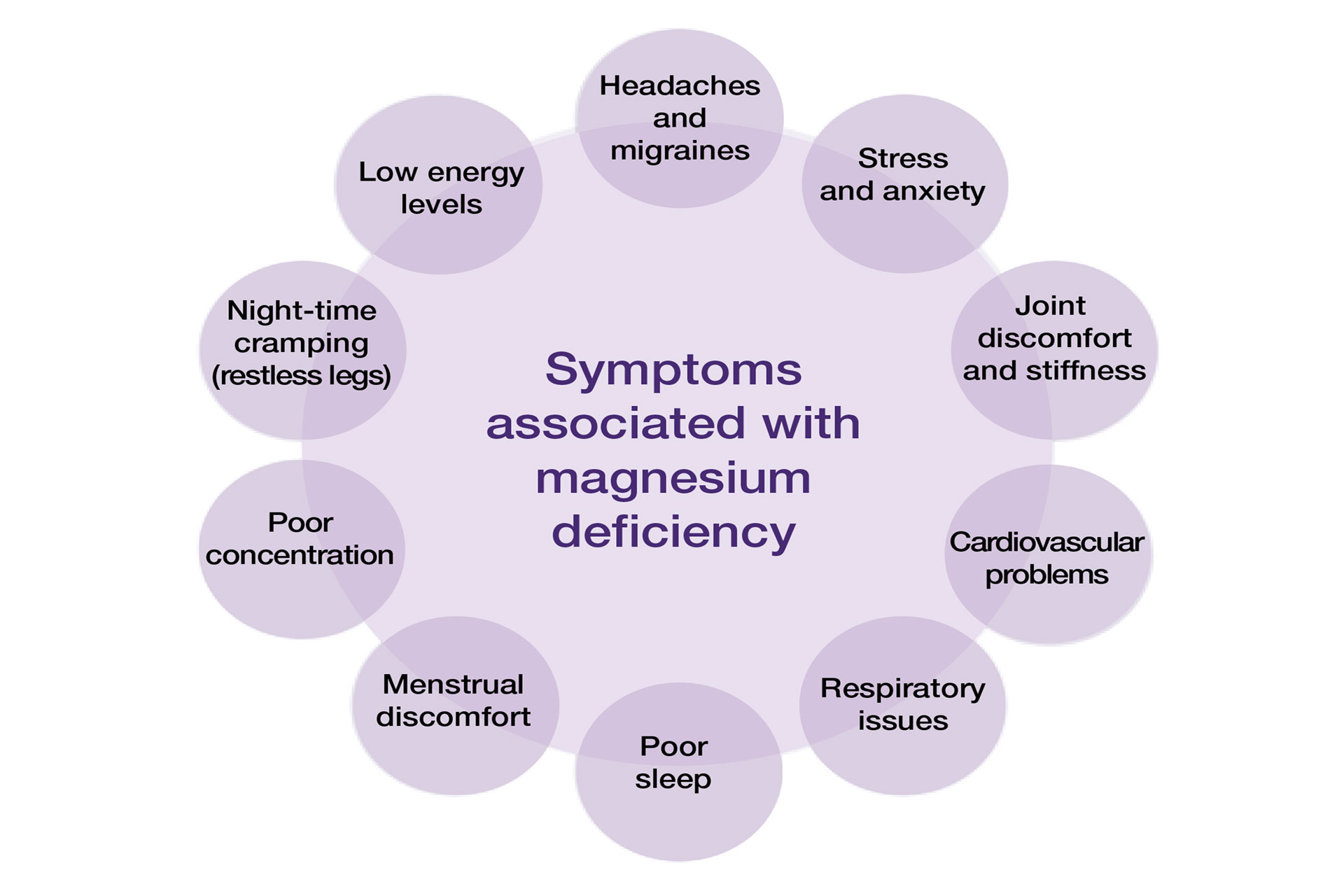
Q1. Low on Magnesium? Here are some of the signs:
Magnesium is the fourth most abundant macromineral or cation (i.e., positive metal ion, Mg2+) in the body. It is important for metabolism, serves as a cofactor in over 300 enzymatic reactions, and regulates about 80% of the body’s biochemical reactions. The Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) of magnesium for adults is between 310 – 420 mg per day, depending on age and gender. While symptomatic magnesium deficiency is uncommon, up to 60-70% of adults in the U.S. may have inadequate intake of magnesium. Subclinical magnesium deficiency has been associated with chronic inflammatory stress conditions, which may contribute to obesity, atherosclerosis, hypertension, osteoporosis, type 2 diabetes, and certain types of cancers. Five signs and symptoms of subclinical deficiency include: muscle cramps, heart palpitations, high blood pressure, fatigue or weakness, and depression, anxiety and/or insomnia.
Q2. From a scientific perspective, how does magnesium relax your body, soothe your mind and elevate your mood?
One of the most frequent signs of magnesium deficiency in the body is hyperexcitability of the nervous system. The amount of magnesium in the brain is highly stable and declines more slowly than in other tissues, so when small decreases happen, it influences neuronal functioning significantly. In people with neurotic anxiety, magnesium levels were shown to be lower in the brain with a higher circulating blood fatty acid/magnesium ratio. When under extreme stress, calcium ions accumulate and the flight/fight hormones, epinephrine and norepinephrine, are released. Magnesium is an important component in this process because it interferes with the calcium channel to reduce calcium ions, thus reducing panic. Magnesium also increases GABA (gamma-amino-butyric acid) receptor activity—an inhibitory neurotransmitter that prevents nerve cells from over-firing to produce a calming effect—and acts as a modulator of glutamate release. Glutamate release is necessary because too much stored glutamate in the brain can cause hyperexcitability and increase the release of stress hormones.
Although the association between magnesium and depression is well documented, the mechanism is unknown. However, magnesium plays a role in many of the pathways, enzymes, hormones, and neurotransmitters involved in mood regulation. For example, a magnesium deficiency in the brain may lower serotonin levels. Serotonin is a powerful neurotransmitter that’s responsible for some of your body’s most important functions. Having low serotonin levels not only causes a depressed mood, it also affects your sleep cycle, appetite, and digestion, among other physical processes.
Additionally, a potential marker of depression is high aldosterone and a potential marker of stress and anxiety is high cortisol levels. Interestingly, magnesium has also been shown in research to inhibit aldosterone and cortisol production by decreasing adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH) secretion.
Since antidepressant drugs have been shown to raise brain magnesium levels, many clinicians have suggested magnesium supplementation to increase the drug’s effectiveness rather than increase dosage of the drug or prescribe another antidepressant.

Q3. Aside from its anti-stress and anti-anxiety capabilities, how does magnesium help support everything from muscles/nerves to heart health?
Every cell in the body needs magnesium. It helps keep muscles strong, nerves alert and your heart in tip-top shape. This is because magnesium plays a key role in the active transport of calcium and potassium ions across cell membranes, a process that is important for nerve impulse conduction, muscle contraction, vasomotor tone and normal heart rhythm. Therefore, a deficiency in magnesium increases the risk of conditions, such as endothelial dysfunction, hypertension, and cardiac arrhythmias.
Q4. What should I look for in a magnesium supplement?
• One that delivers at least 100% of the Daily Value (DV) of elemental magnesium per serving (420 mg)
• If in powder, which is a highly absorbable dosage form, make sure it has zero calories, carbs or added sugar. Look for natural sweeteners like organic stevia (Reb A) instead of the common practice of using sugar, sugar alcohols and/or artificial sweeteners
• No artificial flavors, colors and as mentioned above, no artificial sweeteners since science has shown that exposing your taste buds to these high-intensity sweeteners makes you less receptive to natural sources of sweetness such as fruit. When your taste buds get dulled, you’re more likely to seek out sweeter foods
• Kosher-certified, which validates the quality, integrity and purity of the ingredients in the formula by tracking them back to their manufacturing origin and imposing strict rules on hygienic processes
• Made with non-GMO ingredients †
• Free of common allergens (soy, gluten & milk)
All of these features and benefits are found in Bluebonnet's Simply Calm® Magnesium Powder, which is available in multiple flavors.
† The Non-GMO seal guarantees that the dietary and other ingredients in these formulas are derived from sources that have not been genetically modified using modern biotechnology.










