A: Blood pressure (BP) is defined as the pressure of the blood in the circulatory system; it closely relates to the force and rate of the heartbeat and the diameter and elasticity of the arterial walls. BP rises with each heartbeat and falls when the heart relaxes between beats. While BP can change from minute-to-minute with adjustments in posture, exercise, stress or sleep, it should normally be less than 120/80 mm Hg (less than 120 systolic AND less than 80 diastolic) for an adult age 20 or over. Systole measures the pressure in the arteries when the heart muscle contracts. Diastole measures the pressure in the arteries between heartbeats when the heart muscle is resting between beats and refilling with blood. Below is a chart adapted from the American Heart Association that depicts BP categories:
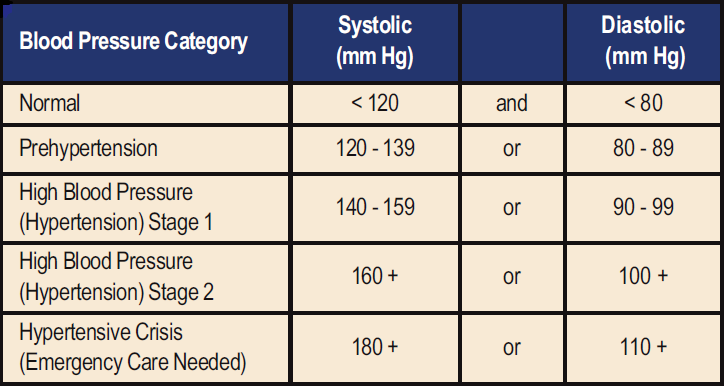 Hypertension (HTN), or chronically elevated BP, is defined as having a systolic pressure greater than 140 mm Hg or diastolic pressure greater than 90 mm Hg. High BP is a problem because the long-term force of the blood against the artery walls can cause damaging effects to the arteries and heart, which can lead to serious health problems including heart attack and stroke.
Hypertension (HTN), or chronically elevated BP, is defined as having a systolic pressure greater than 140 mm Hg or diastolic pressure greater than 90 mm Hg. High BP is a problem because the long-term force of the blood against the artery walls can cause damaging effects to the arteries and heart, which can lead to serious health problems including heart attack and stroke.Q: What are some of the causes of hypertension (HTN)?
A: Causes of HTN can be classified as either primary or secondary: • Primary or Essential Hypertension is high BP that doesn’t have a known secondary cause, which comprises about 90-95% of all hypertensive cases. It is thought to be linked to: • genetics • poor diet • lack of exercise • obesity • insulin resistance • high alcohol intake • high salt intake • stress • low potassium intake • low calcium intake • Secondary hypertension is defined as high BP resulting from a specific underlying condition with a well-known mechanism, such as chronic kidney disease, narrowing of the aorta or kidney arteries, or endocrine disorders, such as excess aldosterone or cortisol.
Q: How does high blood pressure impact health?
A: Left uncontrolled, HTN increases the risk for heart attack, stroke, heart failure, kidney disease, vision loss, sexual dysfunction, angina (chest pain), and many other complications. In fact, HTN is often thought to signify some underlying cardiovascular issues (e.g., plaque build-up/blockage, kidney disease, endocrine disorders, etc.). One can have high BP for years without any symptoms, so it may not be obvious, but HTN is a serious risk factor for cardiovascular morbidity and subsequently, death. This is why BP should be monitored regularly.
Q: What nutrients and lifestyle changes are needed to support normal blood pressure levels?
A: Both lifestyle and dietary modifications can help support healthy BP levels in the body. This should include losing weight if overweight, increasing physical activity, smoking cessation, as well as reductions in sodium and alcohol intake. A well-balanced diet comprised of whole foods, fruits and vegetables is also important. That is why Bluebonnet’s Targeted Choice® Blood Pressure Support is a wholesomely crafted blend of complementary vitamins, minerals and sustainably harvested or wildcrafted herbal extracts, as well as pharmaceutical-grade amino acids plus CoQ10 to help maintain healthy blood pressure levels already within the normal range. The specific ingredients in this unique vegan/vegetarian (soy-, gluten- and milk-free), non-GMO, kosher-certified, whole food-based structure-function formula help support vascular health as follows: ♦
• Hawthorn, taurine, vitamin B6, magnesium and CoQ10 have been shown to help increase excretion of bodily fluids thereby inhibiting sodium and water retention that elevate blood
 pressure. ♦
• Magnesium and hawthorn leaf/flower extract have demonstrated the ability to reduce vasoconstriction by affecting the movement of calcium, causing blood vessels to relax. ♦
• Magnesium, arginine and grape seed extract have been shown to help enhance circulation and blood flow by sending out a signal for vasodilation.♦
• Hawthorn, hibiscus, olive leaf, and grape seed, as well as onion and pumpkin have been shown to decrease hypertensive hormones in the adrenal and pituitary glands by interfering with the conversion of angiotensin II from angiotensin I and inhibiting the degradation of bradykinin, a potent endothelium-dependent vasodilator. ♦
• Grape seed extract, taurine, and CoQ10 exhibit potent antioxidant properties, which is important for heart health. ♦
pressure. ♦
• Magnesium and hawthorn leaf/flower extract have demonstrated the ability to reduce vasoconstriction by affecting the movement of calcium, causing blood vessels to relax. ♦
• Magnesium, arginine and grape seed extract have been shown to help enhance circulation and blood flow by sending out a signal for vasodilation.♦
• Hawthorn, hibiscus, olive leaf, and grape seed, as well as onion and pumpkin have been shown to decrease hypertensive hormones in the adrenal and pituitary glands by interfering with the conversion of angiotensin II from angiotensin I and inhibiting the degradation of bradykinin, a potent endothelium-dependent vasodilator. ♦
• Grape seed extract, taurine, and CoQ10 exhibit potent antioxidant properties, which is important for heart health. ♦ ♦ These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. These products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any disease.
♦ These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. These products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any disease.Jennifer Weinhardt holds a Master of Science in Nutrition
 from Texas Woman’s University and also a Bachelor of Science Degree in Nutrition from Texas A&M University. Mrs. Weinhardt is currently a Research & Development Specialist at Bluebonnet Nutrition where she provides educational training to the sales staff, assists in the launch of new products, and aids in the collaborative writing of marking pieces and technical papers. Jennifer is an advocate for healthy living and the responsible use of supplements.
from Texas Woman’s University and also a Bachelor of Science Degree in Nutrition from Texas A&M University. Mrs. Weinhardt is currently a Research & Development Specialist at Bluebonnet Nutrition where she provides educational training to the sales staff, assists in the launch of new products, and aids in the collaborative writing of marking pieces and technical papers. Jennifer is an advocate for healthy living and the responsible use of supplements.









